Types of Mesothelioma
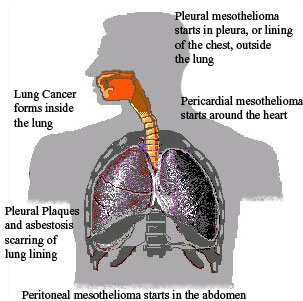
Mesothelioma is a cancer that normally presents in malignant form and results in tumours around vital organs of the body. The mesotelium is a sac that lines and protects vital organs such as the heart and the lungs. And Mesothelioma diseases causes the cell of the lining to become abnormal and malignant.
Mesothelioma comes in three forms including of pleural mesothelioma, perioteneal mesothelioma, and pericardial mesothelioma.
Pleural Mesothelioma :
This is the most commont of mesothelioma where the cancer affects the lungs and the protective lining and cavity of the lungs.
Symptoms :
- Difficulty in breathing;
- Difficulty in swallowing;
- Shortness of breath;
- Persistent coughing;
- Weight loss;
- Fever;
- Coughing up of blood; and
- Rasping.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma :
This is rarer of mesothelioma where the cancer affects the stomach and abdomen. It can start in the abdominal area and spreads to other part of the body.
Symptoms:
- Abdominal pain;
- Abdominal swelling;
- Nause and loss of appetite;
- Vomiting;
- Breathing problem;
- Chest pain;
- Bowel obstruction;
- Anemia;
- Fever; and
- Blood clotting abnormalities.
Pericardial Mesothelioma:
This is the rarest of mesothelioma where the cancer affects to the heart and the cavity surrounds the heart.
Symptoms:
- Chest pain;
- Shortness of breath;
- Trouble breathing;
- Persistent coughing; and
- Palpitations.
The symptoms for all three types of mesothelioma are non specific. It means that they could be the result of a number of more commont diseases associated with the same symptoms. Keep on your eyes and be aware of any mesothelioma symptoms that can be present.
Read more!









